

Thus the increasing number of nucleus attracts the more electrons more tightly towards it and the atomic radius decreases. As you go across a period the atomic radius decreases. A radioactive nucleus EX undergoes spontaneous decay in the sequence Z EX Z1B Z3C Z2D where Z is the atomic number of element X.Ītomic and ionic radius increase as you move down a column group of the periodic table because an electron shell is added to the atoms. Atomic Radii Decrease From Left to Right Across a Period. Periodic trends predict differences between elemental characteristics as you move across the periodic table. Electronegativity not only helps us in studying the chemical properties of an atom but also plays a significant role in studying the electron affinity type of bond formed between atoms the magnitude of the bonds. In atomic physics the Bohr model or RutherfordBohr model presented by Niels Bohr and Ernest Rutherford in 1913 is a system consisting of a small dense nucleus surrounded by orbiting electronssimilar to the structure of the Solar System but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces in place of gravityIt came after the solar system Joseph Larmor model.Ītomic size measured the distance between the nucleus of an atom and the outermost non-valence electrons of the atom. So this means that sometimes atoms with greater atomic mass are smaller in size than.
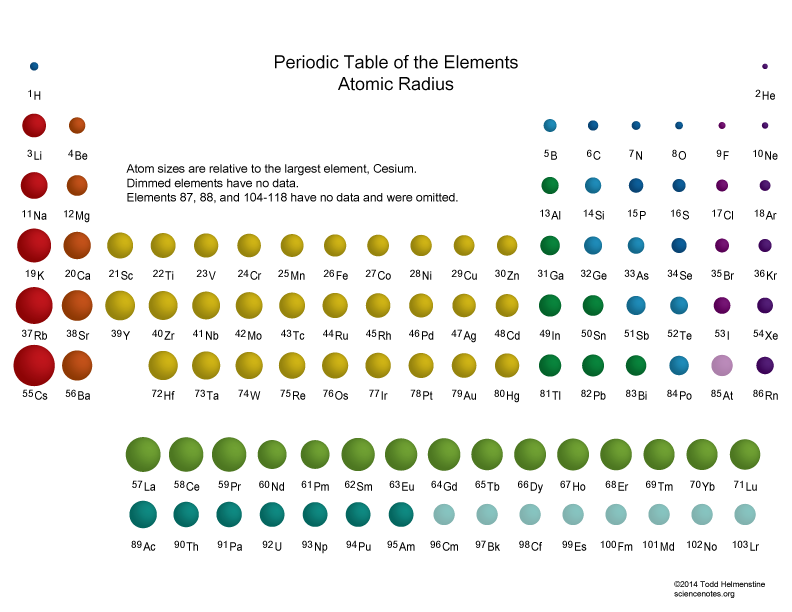
The diagram shows how the atomic radius changes as you go across Period 3. The atomic radii decrease across the periodic table because as the atomic number increases the number of protons increases across the period but the extra electrons are only added to the same quantum shell. Compare wavelength frequency and energy by reading across the three columns.Ĭonsequently the smallest atom is helium with a radius of 32 pm while one of the largest is caesium at 225 pm. Moving from left to right across a period the number of protons and electrons increases while the number of energy shells stay same. This is because the effective positive force of the nucleus also increases drawing in the electrons more tightly. Atomic radius decreases across the period. Atomic Radius Trend 1.Ītomic radius increases down the group. Operation Hurricane was the first test of a British atomic deviceA plutonium implosion device was detonated on 3 October 1952 in Main Bay Trimouille Island in the Montebello Islands in Western AustraliaWith the success of Operation Hurricane Britain became the third nuclear power after the United States and the Soviet Union. The possible decay particles in the sequence are. Between 90000 people are believed to have died from the bomb in the four-month period following the explosion. As you move from left to right across an element period row the ionic radius decreases.Ītomic size decreases as you move across a rowor periodof the table because the increased number of protons exerts a stronger pull on the electrons. Even though the size of the atomic nucleus increases with larger atomic numbers moving across a period the ionic and atomic radius decreases.
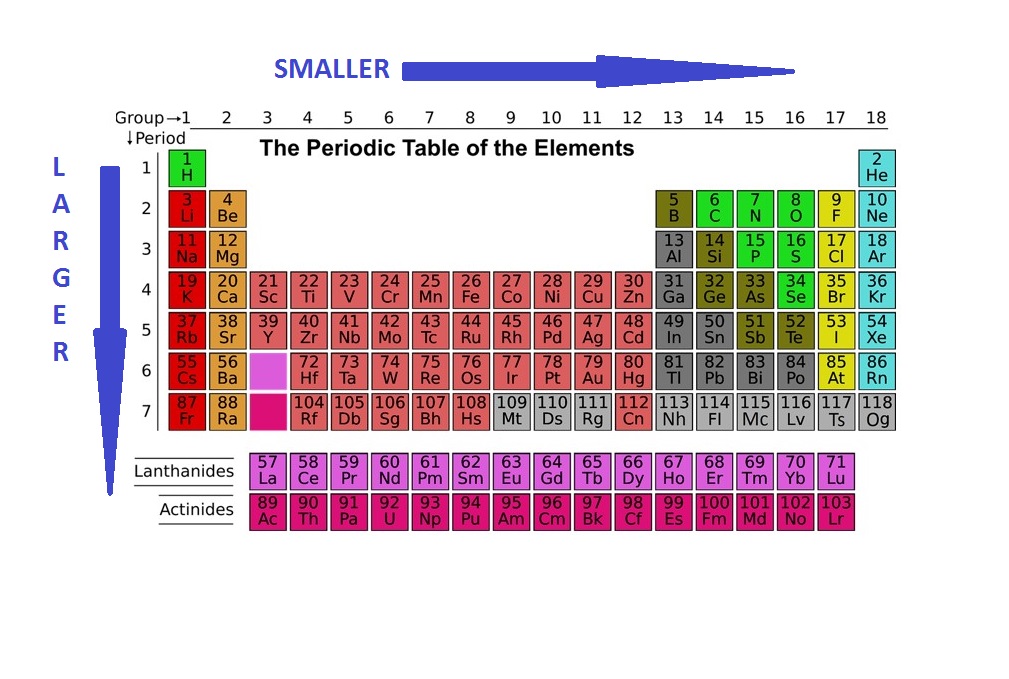
The first atomic radius periodic trend is that atomic size decreases as you move left to right across a period.Ītomic size decreases from.

When an electron is added a new proton is also added to the nucleus which gives the nucleus a. The figures used to construct this diagram are based on. As you go down a group the atomic radius increases. Covalent radii for Si P S and Cl.Ītomic symbols including mass number atomic number and charge Information 4 He a helium nucleus also known as an alpha particle an electron also known as a beta particle when emitted by a nucleus Model The following are two nuclear reaction equations. Within a period of elements each new electron is added to the same shell. Electronegativity in the period table increases as you move from left to right across a period and decreases as you move from top to bottom in a group. Trends In The Periodic Table Chpt 7 1 Atomic Radius Size 2 Ionization Energy 3 Electronegativity The Ionization Energy Periodic Table Covalent Bonding Conversion example for the atomic radius of sodium 186 pm 186 10-12 m 0186 10-9 m 0186 nm 186 pm 186 10-12 m 186 10-10 6 If you would like a more detailed explanation of the changes in first ionisation energy across the period go to the Ionisation Energy and Electronic Configuration tutorial. In one time period become maximum minimum two time So It means frequency of is 2.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
